Cloud technology has completely changed how companies run their operations, store data, and create digital products. From startups to large corporations, cloud-based applications and services have become the backbone of modern IT strategies. The secret behind this transformation is a well-structured cloud computing architecture that ensures smooth integration of storage, computing power, networking, and security.
In this guide, we’ll explore how cloud computing architecture works, its different service models, and examples of how businesses are using it to innovate.
What is Cloud Computing Architecture?
A cloud computing architecture is the framework that brings together all the key components required to deliver cloud services. It typically follows a cloud computing service-oriented architecture (SOA) model, where different services communicate and work together seamlessly.
The architecture usually includes:
- Front-end layer: Interfaces and applications used by the client.
- Back-end layer: Databases, storage, and servers that process and store data.
- Network infrastructure: Connects front-end and back-end services.
- Cloud security solutions: Safeguard sensitive data and protect against cyber threats.
A well-planned cloud computing architecture design allows organizations to build scalable, secure, and cost-efficient systems for software application development and deployment.
Why Businesses Are Choosing Cloud Computing
Switching to the cloud offers numerous advantages over traditional on-premises systems:
- Scalability on demand – Resources can be expanded or reduced instantly.
- Lower IT costs – Pay only for what you use.
- Remote accessibility – Access your data and apps from any location with an internet connection.
- Faster deployment – Speed up product launches and application updates.
- Stronger security – Use advanced cloud security tools to protect sensitive data from cyber threats.
For businesses aiming to stay competitive, cloud adoption is no longer optional, it’s essential.
Cloud Deployment Models
Choosing the right deployment model is an important part of cloud architecture planning.
1. Public Cloud
Hosted and managed by third-party providers such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
Example: A startup using AWS for hosting its website and database.
2. Private Cloud
A private cloud provides exclusive infrastructure for one organization, ensuring greater privacy, control, and customization.
Example: A healthcare company storing patient records on a secure private cloud.
3. Hybrid Cloud
Combines public and private clouds, allowing data and apps to move between them as needed.
Example: An e-commerce store running customer-facing services on a public cloud while keeping payment systems private.
4. Multi-Cloud
Uses multiple cloud providers to prevent vendor lock-in and increase flexibility.
Example: A global corporation distributing workloads across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
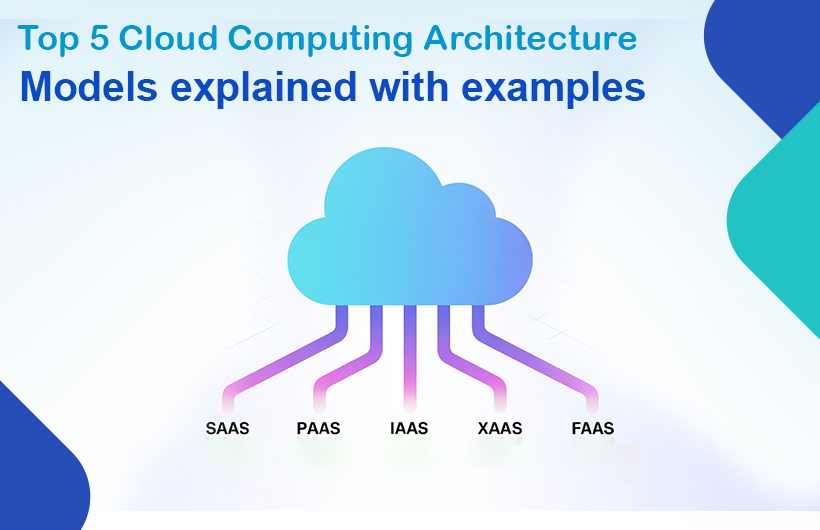
Types of Cloud Service Models
In a cloud computing service-oriented architecture, services are delivered through different models based on business needs.
1. Software as a Service (SaaS)
Delivers ready-to-use software over the internet without installation or maintenance.
Examples: Google Workspace, Zoom, Dropbox.

Benefits:
- No hardware setup required.
- Automatic updates.
- Access from any device with internet connectivity.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Provides a cloud-based environment for software application development, testing, and deployment.
Examples: Microsoft Azure App Service, Heroku, Google App Engine.

Benefits:
- Faster development cycles.
- No need to manage physical infrastructure.
- Easy scalability and integration tools.
3. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Offers virtualized computing resources like servers, storage, and networks.
Examples: cloud-based virtual machine services include Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure VMs, and Google Compute Engine.

Benefits:
- Full control over infrastructure.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing.
- High flexibility for custom setups.
4. Anything as a Service (XaaS)
Covers all services that can be delivered via the cloud.
Examples: Cloud storage and AI delivered as services.

Benefits:
- Flexible and customizable solutions.
- Cost-efficient for specialized needs.
5. Functions as a Service (FaaS)
Also called serverless computing, it runs functions in response to events without managing servers.
Examples: AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions.

Benefits:
- Automatic scaling.
- Lower costs for event-driven workloads.
- Minimal operational complexity.
Practical Examples of Cloud Service Usage
- SaaS: Businesses using Slack for team communication.
- PaaS: Developers building mobile apps on Firebase.
- IaaS: A game development company hosting servers on AWS EC2.
- FaaS: An online store using AWS Lambda for real-time inventory updates.
Final Thoughts
Cloud computing has redefined how businesses operate, enabling faster innovation, cost savings, and global accessibility. By understanding cloud computing architecture design and selecting the right service model, organizations can create reliable, secure, and future-ready systems.
How Monarch Innovation Can Support Your Cloud Journey
Monarch Innovation delivers comprehensive solutions across cloud architecture, service-oriented systems, software development, and cloud security empowering businesses with scalable, secure, and customized digital infrastructure. Whether you’re planning a migration, building a new cloud-based platform, or strengthening security, our experts deliver customized, scalable, and performance-driven results.