In the complex world of product development, where innovation is the driving force, two dynamic disciplines, Industrial Design and Mechanical Engineering, play pivotal roles. These two fields, seemingly distinct, come together to shape the products we interact with every day. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the differences between Industrial Design and Mechanical Engineering, supported by real-world examples. Moreover, we will introduce you to Monarch Innovation, your trusted partner in achieving the perfect balance between aesthetics and functionality.
Industrial Design: Where Art and Utility Converge
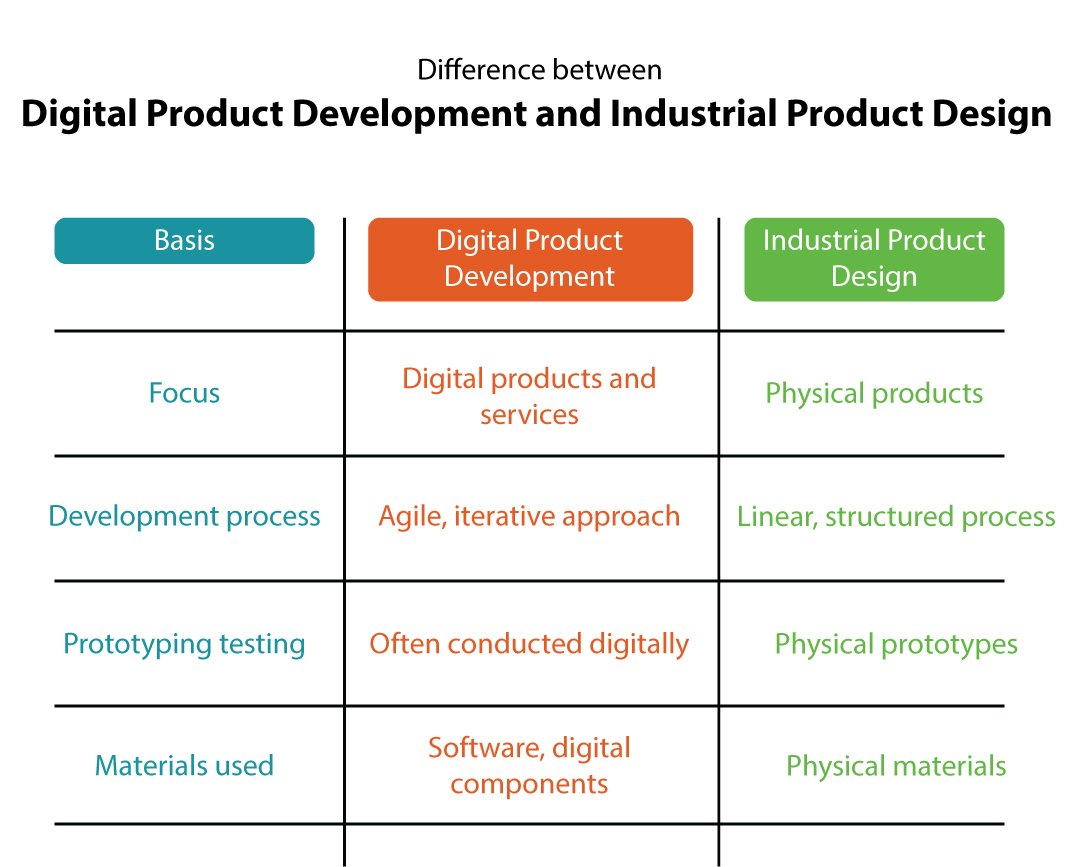
Industrial design is the creative heart of product development, blending aesthetics and functionality. Drawing from principles of ergonomics and unbounded creativity, industrial designers craft products that are not just practical but also visually captivating. They often follow an outside-in approach, prioritizing user experience and aesthetics.
Example: Think of the iPhone—a marvel of industrial design. Its sleek, user-friendly design and seamless integration of technology epitomize user-centric principles. Apple’s unwavering commitment to design has made its products iconic.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Precision in the Digital Realm
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) serves as the digital realm where engineers and designers transform abstract concepts into precise, three-dimensional models. This versatile tool is akin to a craftsperson’s toolkit, used to give life to intricate ideas.
Example: The Burj Khalifa, the world’s tallest skyscraper, heavily relied on CAD technology. It allowed engineers and architects to meticulously plan and execute the complex geometries and structural elements of the building.
Mechanical Engineering: The Science of Functionality and Reliability
Mechanical engineering forms the backbone of functionality and reliability. Rooted in scientific principles, mechanical engineers comprehend how objects respond to various forces and conditions. In the realm of product design, they take an inside-out approach, prioritizing performance, reliability, and manufacturability.
Example: The Boeing 787 Dreamliner showcases the prowess of mechanical engineering. Advanced materials, aerodynamic design, and innovative systems ensure fuel efficiency, reliability, and passenger comfort.
Choosing the Right Path: Project-Driven Decision
In today’s multifaceted landscape, industrial design firms may encompass mechanical expertise, while mechanical engineering company may house design-savvy professionals. CAD administrators often serve as versatile bridge builders, wielding the technical acumen needed to transform abstract ideas into tangible reality.
Example: When designing a high-end sports car, aesthetic appeal reigns supreme. Manufacturers like Ferrari engage industrial designers to craft visually stunning vehicles. However, beneath the surface, mechanical engineers ensure the car’s engine, suspension, and other components deliver top-tier performance and safety.
Pros and Cons: Industrial Design vs. Mechanical Engineering
Industrial Design:
Pros:
- Aesthetic Excellence: Industrial design prioritizes aesthetics, resulting in visually captivating and user-friendly products.
- Innovation: Industrial designers push creative boundaries, leading to groundbreaking concepts that capture attention.
- Market Differentiation: Well-executed industrial design sets products apart, fostering brand loyalty and market success.
Cons:
- Risk of Impracticality: Pursuing aesthetics and innovation may lead to challenging manufacturing processes and increased production costs.
- Limited Focus: Industrial design may prioritize form over function, potentially overlooking critical engineering considerations.
- Subjectivity: Aesthetic preferences vary widely, making it challenging to create universally appealing designs.
Mechanical Engineering:
Pros:
- Functional Excellence: Mechanical engineering ensures products perform reliably and efficiently under various conditions.
- Reliability: Rigorous testing and analysis lead to product durability, reducing failures and recalls.
- Manufacturability: Mechanical engineers consider ease of manufacturing, leading to cost-effective production processes.
Cons:
- Aesthetic Sacrifice: Mechanical engineering may prioritize function over form, potentially resulting in aesthetically lacking products.
- Less Innovation in Form: A strong focus on functionality may stifle creativity in product aesthetics, leading to a lack of differentiation.
- Complexity: Meticulous engineering can lead to longer design and development timelines.
Conclusion: Achieving the perfect balance
The distinctions between industrial design and mechanical engineering are not mere technicalities but the pillars upon which product development stands. It’s a world where creativity and precision converge, and the unique needs of your project should guide your choice.
In an ideal scenario, collaboration between industrial designers and mechanical engineers strikes a harmonious balance, resulting in products that excel in both form and function.
This is where Monarch Innovation, your trusted partner, comes into play.
Monarch Innovation is more than a company; it’s your trusted partner in crafting the perfect blend of aesthetics and functionality. With a team of seasoned professionals and cutting-edge resources, Monarch Innovation redefines the boundaries of what’s possible in design and engineering.
With Monarch Innovation by your side, you can seamlessly integrate the artistry of industrial design with the precision of mechanical engineering to breathe life into your vision.
In this intricate symphony of creativity and precision, Monarch Innovation is the conductor, orchestrating your journey toward innovative excellence. As you embark on your path of product development, Monarch Innovation is poised to illuminate your way, ensuring your vision becomes a reality where aesthetics and functionality coexist harmoniously.
FAQs
Can a mechanical engineer do industrial design?
Yes, a mechanical engineer can transition into industrial design with additional training in creative design principles and aesthetics. Many engineers successfully cross over into industrial design roles.
Is industrial design the same as mechanical engineering?
No, industrial design and mechanical engineering are distinct fields. Industrial design focuses on aesthetics, user experience, and form, while mechanical engineering deals with the technical aspects of product functionality and structural design.
What does mechanical & industrial engineering do?
Mechanical engineering involves designing, analyzing, and developing mechanical systems, machines, and devices, while industrial engineering optimizes processes, systems, and workflows to improve efficiency and productivity in various industries.
Can I be an industrial designer with an engineering degree?
Yes, having an engineering degree can be a valuable asset in industrial design, as it provides a strong foundation in problem-solving and technical understanding. Many industrial designers hold engineering degrees or have engineering backgrounds. Additional training in design principles may be necessary for a smooth transition.